Overview of Row Data Storage and Column Data Storage
Using relational databases in general file-based
data storage. However, Column-based storage is more suitable for many business
applications. SAP HANA supports both column-based storage and file-based and is
particularly suitable for archiving based on columns optimized.
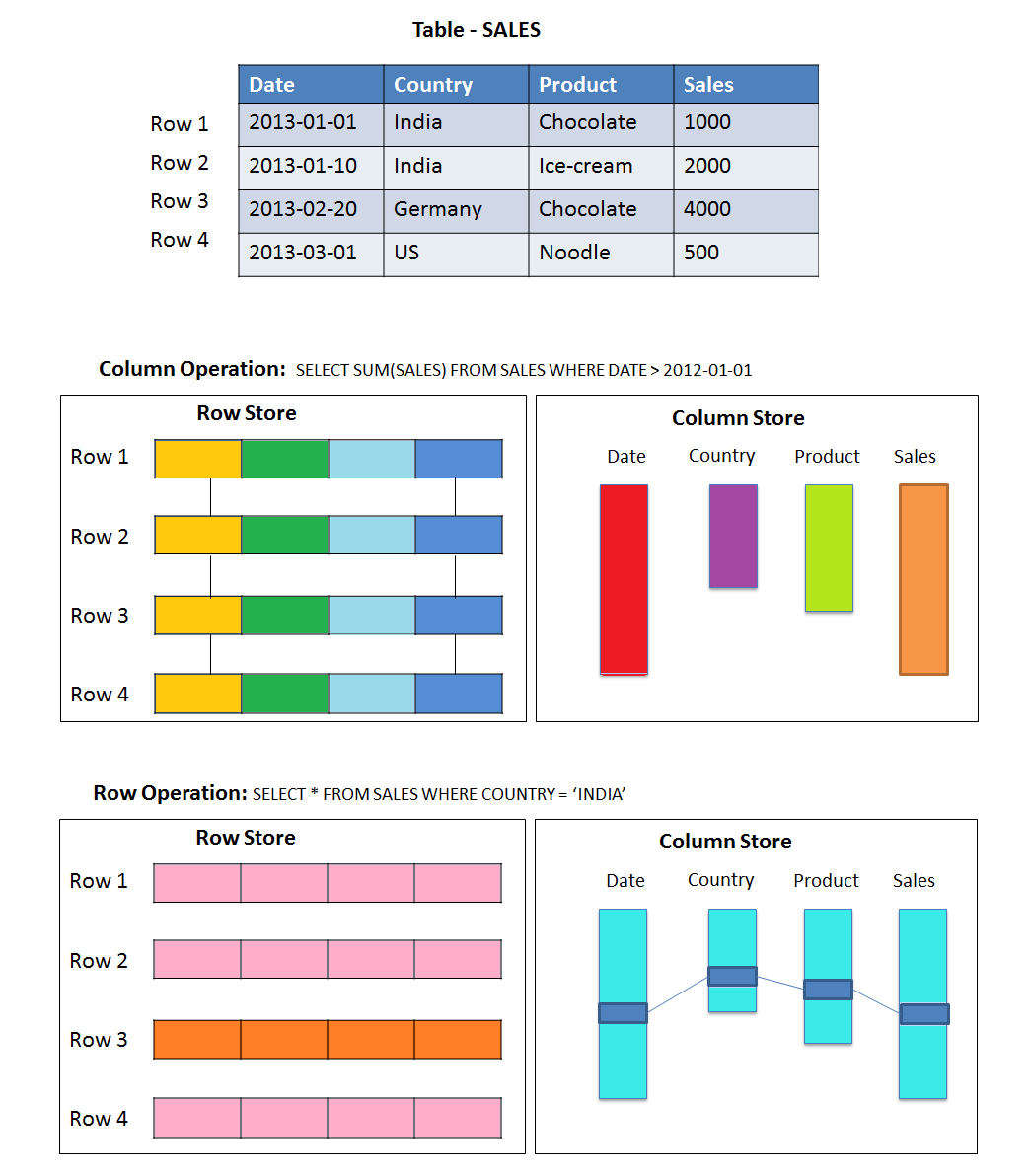
As shown in the figure, a database
table is a conceptual structure of two-dimensional cells are arranged in rows and columns.
Since the linear structure of
computer memory, there are two possibilities for sequences stored in the memory
location the values of
neighboring cells:
Row Storage – Save
the table entries in a series of rows.
Column Storage – Remember
table entries (ie) entries of a column stored in contiguous memory locations in
a series of columns.
Traditional databases store data in
simple lines. The HANA in-memory
database data in both rows and columns. It is this combination of the two projections
bearings, which generates the speed, flexibility and performance of the
database HANA.
Advantages of column-based tables:
Faster Data Access:
Only the relevant columns to be read in the selection of a
query. Each of the columns can be used
as an index.
Better Compression:
Data storage column allows the
highly efficient compression, as most of the columns only some different values
(compared
to the number of rows).
Better parallel Processing:
In a column store, the data is
already split vertically. This means that the operations of several columns can
be easily processed parallel. If more than one column to be aggregated or
research, each of these operations can be assigned to a different processor
core
Advantages and disadvantages of row-based tables:
Row
based tables have advantages in the following circumstances:
·
The
application process requires only a single record at a time (many select and /
or updates of individual records).
·
The
application must usually have access to a complete record (or row).
·
The
table has a small number of rows (for example, configuration tables, system
tables).
Row based tables have dis-advantages in the following circumstances:
In the case of analytical
applications in which aggregation can be used is the search request and
processing. In row tables to read all the data in a row, even if the
application can be to access data from some columns based.
Which type of tables should be preferred – Row-based or Column-based?
File-based storage, in the case of
analytical applications involving the use of aggregations and research and
rapid processing is required are not good. In row tables to read all the data
in a row, even if the application can be to access data from some columns
based. Therefore, these queries on large data sets take a lot of time.
Columnar tables, this information is
recorded are physically next to each other, the speed of the data samples determined
significantly.
The following example shows the use
of different columns and rows storing and positions it with respect to requests
for row and column. Archiving column is very useful for OLAP queries (queries
using the SQL aggregate functions), because these requests they get only a few
attributes of every data item. But for traditional OLTP queries (queries that
do not use SQL aggregate functions ), it
is more advantageous to store all the attributes of side - by-side in online
tables . HANA combines the advantages of both the row and column memory tables
Conclusion:
To enable fast on-the-fly
aggregation, ad hoc reporting, and benefit from compression mechanisms,
transaction data is stored in a table based on columns recommended.
The connection to the SAP HANA
database allows tables with row-based tables based on columns. However, it is
more efficient, the tables are arranged in the same row or columns are memory.
For example, personal data, which often came with transaction data columns in
the base tables must be saved.


No comments :
Post a Comment